A Guide to Recognizing the Early Signs of Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer is a relatively rare but serious condition that affects the external female genital area. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes, yet many women remain unaware of the warning signs. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and screening options can empower women to seek timely medical attention. This guide provides essential information about recognizing early signs of vulvar cancer and the importance of proactive health monitoring.
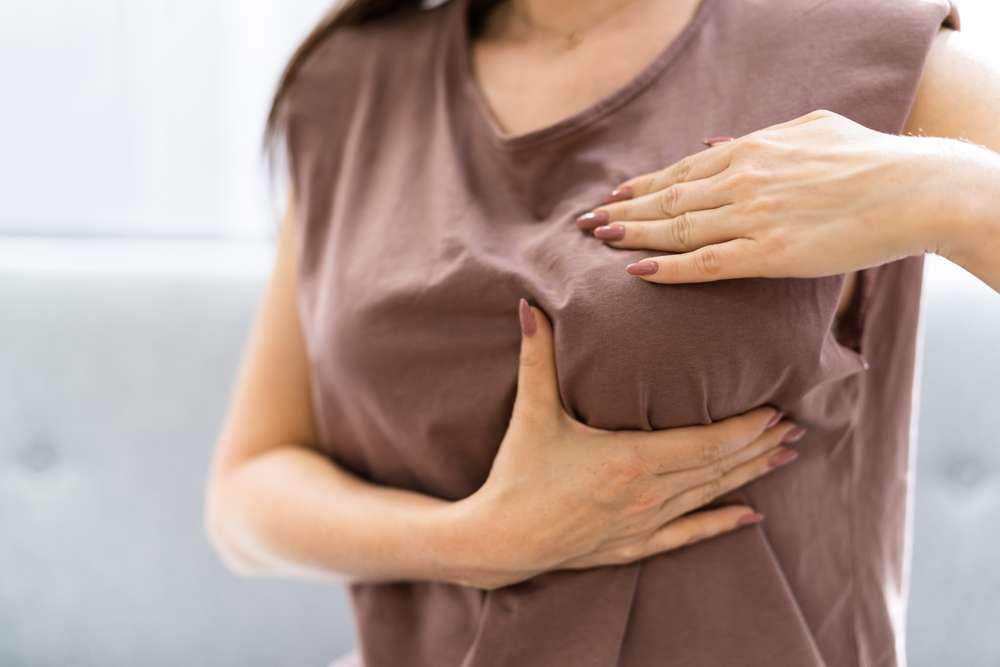

Vulvar cancer develops in the vulva, the outer part of the female reproductive system that includes the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening. While it accounts for a small percentage of gynecologic cancers, awareness of its early symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment. Women of all ages should be familiar with changes in this area that may warrant medical evaluation.
What Are the Early Symptoms of Vulvar Cancer?
Recognizing early symptoms of vulvar cancer can be challenging, as initial signs may resemble other benign conditions. The most common early warning sign is persistent itching in the vulvar area that does not respond to typical treatments. Women may also notice changes in skin color, with areas appearing darker, lighter, or redder than surrounding tissue. A lump or thickened patch of skin on the vulva is another significant indicator that should not be ignored.
Other symptoms include a persistent sore or ulcer that does not heal within a few weeks, tenderness or pain in the vulvar region, and bleeding that is not related to menstruation. Some women experience a burning sensation during urination or notice unusual discharge. Any wart-like growths or mole-like spots that change in appearance should also prompt immediate medical consultation. Early-stage vulvar cancer may present with subtle symptoms, making regular self-examinations and routine gynecological check-ups essential.
How Does Screening Help with Prevention?
Cervical and vulvar cancer screening plays a vital role in early detection and prevention. While there is no standard screening test specifically for vulvar cancer like there is for cervical cancer, regular pelvic examinations allow healthcare providers to identify abnormal changes. During these examinations, gynecologists visually inspect the vulvar area for lesions, discoloration, or other suspicious features.
For cervical cancer, Pap smears and HPV testing are standard screening methods that can also provide insights into overall gynecologic health. Since human papillomavirus (HPV) is a risk factor for both cervical and vulvar cancers, HPV vaccination and regular screening are important preventive measures. Women should discuss their individual risk factors with their healthcare provider to determine an appropriate screening schedule. Self-examination at home, where women visually and manually check for changes in the vulvar area, can complement professional screenings.
What Role Do Prevention Programs Play?
Women’s cancer prevention programs offer comprehensive services designed to reduce cancer risk and promote early detection. These programs typically include education about risk factors, screening services, HPV vaccination initiatives, and support for lifestyle modifications that may lower cancer risk. Many programs focus on underserved populations who may have limited access to regular gynecologic care.
Prevention programs often provide resources such as informational materials, community outreach, and affordable or free screening services. They emphasize the importance of regular check-ups, self-awareness, and prompt medical attention for concerning symptoms. Some programs also offer genetic counseling for women with family histories of gynecologic cancers. Participation in these programs can significantly improve health outcomes by ensuring women receive timely screenings and appropriate follow-up care.
When Should You Consult Gynecologic Oncology Specialists?
Gynecologic oncology specialists are physicians with advanced training in diagnosing and treating cancers of the female reproductive system. If initial screening or examination reveals suspicious lesions or if vulvar cancer is diagnosed, referral to a gynecologic oncology specialist is typically recommended. These specialists have expertise in performing biopsies, staging cancer, and developing comprehensive treatment plans.
Consultation with a specialist is particularly important when dealing with pre-cancerous conditions such as vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), which may progress to invasive cancer if left untreated. Gynecologic oncologists work closely with other healthcare professionals, including pathologists, radiologists, and surgical teams, to provide coordinated care. They can offer the most current treatment options, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, tailored to each patient’s specific situation.
What Treatment Options Are Available?
Treatment for vulvar cancer depends on the stage of disease, location of the tumor, and overall health of the patient. Early-stage vulvar cancer may be treated with surgical excision, where the cancerous tissue and a margin of healthy tissue are removed. For more advanced cases, more extensive surgery may be necessary, potentially including removal of lymph nodes.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells and may be used before surgery to shrink tumors or after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells. Chemotherapy, which uses drugs to kill cancer cells, may be recommended for advanced vulvar cancer or when cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Some patients may receive a combination of these treatments. Treatment facilities with specialized gynecologic oncology departments typically offer access to multidisciplinary teams and advanced treatment technologies.
| Treatment Type | Description | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Excision | Removal of cancerous tissue with healthy margins | Early-stage localized cancer |
| Radical Vulvectomy | Extensive removal of vulvar tissue | Advanced localized cancer |
| Radiation Therapy | High-energy beams targeting cancer cells | Pre-surgery tumor reduction or post-surgery treatment |
| Chemotherapy | Systemic drug treatment | Advanced or metastatic cancer |
| Combination Therapy | Multiple treatment modalities | Various stages depending on individual factors |
How Can Women Advocate for Their Health?
Proactive health advocacy begins with education and self-awareness. Women should familiarize themselves with normal vulvar anatomy and regularly perform self-examinations to detect changes early. Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers about any concerns, no matter how minor they may seem, is essential. Women should not hesitate to seek second opinions or request referrals to specialists when needed.
Keeping up with recommended screening schedules, maintaining HPV vaccination status, and participating in prevention programs are important steps. Lifestyle factors such as avoiding tobacco use, maintaining a healthy immune system, and practicing safe sex can also reduce cancer risk. Women with symptoms should seek medical attention promptly rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. Early intervention consistently leads to better treatment outcomes and improved quality of life.
Understanding the early signs of vulvar cancer and taking advantage of available screening and prevention resources empowers women to take control of their gynecologic health. While vulvar cancer is relatively uncommon, awareness and vigilance can make a significant difference in outcomes. Regular medical care, self-examination, and prompt attention to concerning symptoms remain the cornerstones of early detection and successful treatment.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.